View Article as Single page
The 12¼-in. section was drilled with statically underbalanced mud of 12 to 9 ppg with bottomhole equivalent circulating density (BHECD) ranging from 14 to 14.6 ppge. There were no well control events and a stable drilling window was maintained through the 1,263 ft (385 m) drilled. Although MPD was not needed, it was able to provide valuable data that was not available from logs. The section provided the first opportunities to conduct dynamic leak off tests (DLOT) and dynamic pore pressure determination tests (DPPDT).
During MPD operations in the 8 ½-in. section, there were five minor well events that resulted in closure of the annular preventer. Each was related to either equipment failure or anticipated high gas levels resulting from operation activities. In the first instance, a top drive system swivel packer failure resulted in a decision to pull back five stands of pipe to the shoe. The pipe movement resulted in swabbing and masked volume outflow trends. The second event involved a rig power failure, and event three occurred when gas levels reached 29% at the mud loggers and 58% at the Weatherford GC-Tracer gas chromatograph located downstream from the choke manifold and upstream from the MGS. Gas was expected due to testing procedures and connections, and was not the result of a gas influx. Event four was precipitated by line vibration that sheared crossover pipework, and event five occurred when the pump feed failed.
Critical testing
Use of DLOT and DPPDT was critical in defining drilling window limits. The data informed decisions on what BHECD to hold. Hole strength was also improved with stress gauge material pumped in a DLOT mud squeeze.
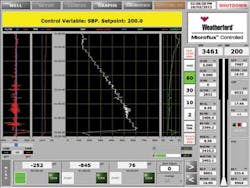
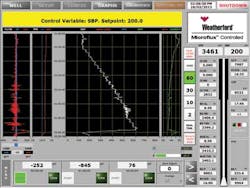
In conducting DLOTs, connections were carried out with SBP automatically increasing to replace frictional losses and maintain constant BHP as mud pump pressure was reduced. SBP was achieved by flowing the auxiliary pump through the MPD chokes. As much as 1,200 psi SBP was required when the mud pumps were fully stopped.
The DLOTS were performed using rig pumps to pump through the bit while rotating the drillstring. This method results in lower required surface pressures, which enhances safety and surface equipment life. The MPD system provided SBP to eliminate non-productive time (NPT) and use of the BOP. Flow meters in the MPD system confirmed the fracture gradient by recording small fluid losses. DLOTS were conducted several times in a section to measure the weakest point rather than assuming the casing shoe was the weakest point.
Similarly, DPPDT were performed using mud pumps and rotating the string. No additional MPD rig up was required. Surface pressure was reduced in stages until a small influx was seen via the flow meter. The influx was safely circulated out of the well through the MGS. Along with DLOT, the test was valuable in determining the actual drilling window.
Rare operations
Relatively rare closed loop coring operations were performed in the 8½-in. section. The closed loop system was used to maintain early kick loss detection (EKLD) and keep BHP constant during coring. The system had no affect on the coring operations. Extra tripping with a large gauge BHA was required and swabbing was counteracted with SBP after a mud cap was placed.
Closed loop wireline, also a seldom-used operation, contributed significantly to the safety of operation. The system was used to maintain EKLD and prevent swabbing when pulling out of the hole by applying SBP. The closed loop system was created without using rig well control equipment and while allowing the rig to maintain flow detection capabilities. In addition, the RCD provided a solid anchor for the wireline grease head.
Closed loop statically underbalanced cementing was also performed on the well. Cementing involved varied surface pressures due to different fluid weights in the hole to maintain constant BHP. The closed loop system yielded more precise spacer and slurry displacements, and enabled detection of induced fractures while cementing. Annular backpressure, applied using a choke or backpressure pump, allowed pressure to be adjusted throughout the cementing process.
Unconventional solutions
Drilling the West Africa well was a challenge that had stood since the 1970s, when it became obvious that conventional drilling methods were not adequate for the task.
The application of MPD methods and closed loop drilling technology provided an unconventional well construction solution. The successes and versatility of the project provides a path forward for many prospects that have previously been undrillable.