Spectrum starts multi-client 2D seismic survey offshore Mozambique
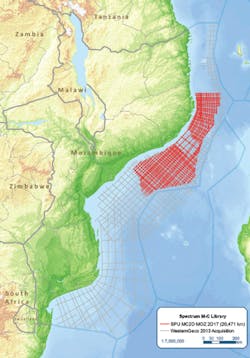
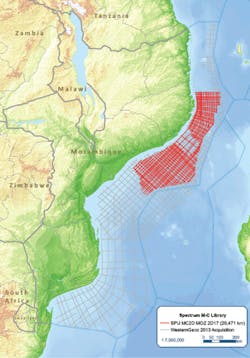
The survey is specifically designed to image the subsurface potential in the southern Rovuma basin and the western flanks of the Kerimbas Graben, west of the Davie Fracture Zone. (Courtesy Spectrum)
Spectrum, on behalf of the Institute of National Petroleum (INP), has started a 2D multi-client seismic survey offshore Mozambique. This new 2D seismic program of up to 19,000 km (11,806 mi) will be undertaken using a 10,000-m (32,808-ft) offset with continuous recording to enable extended recording lengths and high fold data. Gravity and magnetic data will be acquired in conjunction with seismic data to allow for independent verification of structure.
The survey is specifically designed to image the subsurface potential in the southern Rovuma basin and the western flanks of the Kerimbas Graben, west of the Davie Fracture Zone, providing a more detailed understanding of the prospectivity in this region. Potential targets, identified following recent studies in the area, include Cretaceous and Tertiary turbidites and buried canyon plays.
The survey will also image the syn-rift structures and Late Cretaceous pro-delta stacked turbidite sequences in the northeast Zambezi Depression. The data will be processed with PSTM, PSDM, and Broadband products with first deliveries in early 2Q 2018. This survey will be carried out in partnership with WesternGeco and is supported by industry funding. The survey is being acquired to complement existing 2013 seismic located in the Mozambique Channel area.
Graham Mayhew, executive vice president of the Africa Region, said: “This new multi-client survey will play a key role in refining our understanding of the hydrocarbon potential offshore Mozambique between the southern Rovuma basin and the northeast of the Zambezi Delta, and accelerate exploration in an area considered to be significantly more oil-prone.
“In addition, the data will also provide the basis for future license rounds as planned by INP.”
CGG to conduct more airborne surveys offshore Mexico
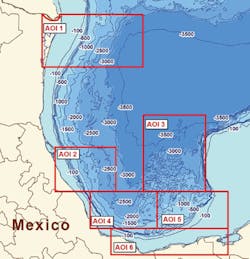
CGG Multi-Physics has completed acquisition, processing, and interpretation of a multi-client airborne gravity and magnetic survey of about 38,000 line km (23,612 mi) over the Perdido foldbelt. Data acquisition of area AOI 1 was completed in December 2016 using a Basler geophysical survey aircraft. This survey is the first of six areas to be acquired in a wider program totaling 200,000 line km (124,274 mi) across the Mexican Gulf of Mexico. Additional acquisition in the other areas is planned for 2018.
Location of AOI 1 and other areas proposed in CGG’s multi-client airborne GravMag program offshore Mexico. (Courtesy CGG)
The newly acquired Perdido foldbelt data, the company claims, has shown an interesting correlation of significant discoveries along the flanks of basement topography. The data and interpretation will help explorers map crystalline basement, which is not well imaged by seismic, to construct an improved Earth Model. The airborne survey also collected continuous data through the “transition zone” from the marine environment to onshore.
The comprehensive interpretation, combining this new data set with available geologic and geophysical data, was undertaken by CGG’s in-house interpretation team in Houston. A full geophysical interpretation report, which includes mapping of basement, sediment and any intrusives or salt which may be present, will provide important insights to exploration and de-risking of prospective areas by oil companies.
Greg Paleolog, senior vice president, Multi-Physics, CGG, said: “The results of this first survey in our wider airborne GravMag program offshore Mexico reinforce our belief that this extensive new program, when combined with our other seismic, geologic and satellite multi-client data in Mexico, will give the industry access to a unique geoscience library to support the future exploration and economic development of this high-potential area.”